Blood Thinner: What It Is, How It Works, and What You Need to Know
When your blood thickens too much, it can form clots that block arteries or veins—leading to strokes, heart attacks, or pulmonary embolisms. That’s where a blood thinner, a medication that reduces the blood’s ability to clot. Also known as anticoagulant, it doesn’t actually make your blood watery—it just slows down the clotting process to keep things flowing safely. If you’ve been told you need one, you’re not alone. Millions use them every day after heart surgery, for atrial fibrillation, or after a deep vein thrombosis.
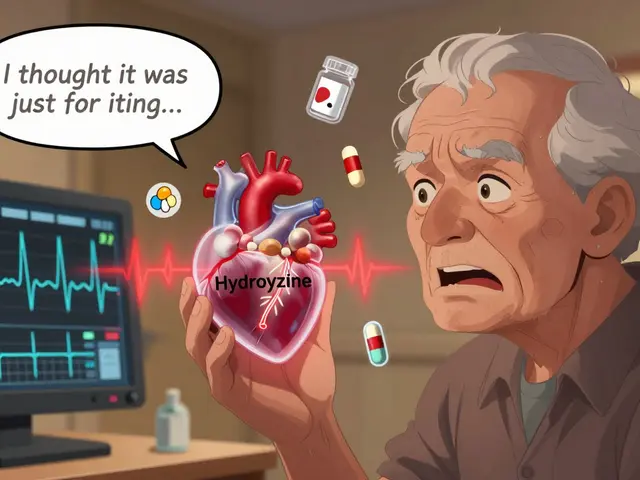
Not all blood thinners are the same. Some, like warfarin, a long-used oral anticoagulant that requires regular blood tests to monitor, work by blocking vitamin K, which your body needs to make clotting factors. Others, like aspirin, a daily low-dose option that thins blood by stopping platelets from sticking together, are milder and often used for prevention in people with higher heart disease risk. Then there are newer options like rivaroxaban or apixaban—faster acting, fewer food interactions, but usually more expensive. The right one depends on your condition, other meds, lifestyle, and even your diet.
People often worry about bleeding risks, and that’s valid. A cut that won’t stop bleeding, unusual bruising, or dark stools can be warning signs. But skipping your blood thinner because you’re scared is riskier. The goal isn’t to stop clotting completely—it’s to find the sweet spot where clots won’t form, but you still bleed normally if you cut yourself. That’s why sticking to your schedule, avoiding certain supplements like high-dose fish oil or ginkgo, and telling every doctor you see that you’re on a blood thinner matters more than you think.
You’ll find posts here that break down how warfarin compares to other options, what to watch for when mixing it with other meds, and how to buy it safely online without falling for scams. There’s also info on how these drugs interact with common conditions like high blood pressure, liver issues, or even travel. No fluff. No guesswork. Just clear, real-world advice from people who’ve been through it.

How Apixaban Reduces Stroke Risk in Atrial Fibrillation Patients
Apixaban is a leading blood thinner for atrial fibrillation patients, reducing stroke risk by 21% and bleeding by 31% compared to warfarin. It's easier to use, safer for seniors, and doesn't require regular blood tests.
View More