How to Treat Hypoglycemia: Quick Fixes, Medications, and Prevention Tips
When your blood sugar, the amount of glucose in your bloodstream. Also known as hypoglycemia, it occurs when levels drop below 70 mg/dL and your body starts to panic. Symptoms hit fast: shaking, sweating, confusion, dizziness, or even passing out. If you have diabetes, you’ve probably felt this before. But even people without diabetes can get low blood sugar from skipping meals, drinking alcohol, or taking certain meds. The key isn’t just knowing it’s happening — it’s knowing how to fix it before it turns dangerous.
Quick treatment means fast-acting sugar. Glucose tablets, a concentrated form of sugar designed to raise blood sugar in minutes. They’re better than candy because they’re measured, fast, and don’t come with fat or protein that slows absorption. Four glucose tabs, 4 ounces of juice, or a tablespoon of honey — any of these can bring you back up in 15 minutes. Then eat a snack with protein and carbs, like peanut butter on toast, to keep your sugar stable. If you’re on insulin or sulfonylureas, your doctor should have given you a glucagon injection, a emergency medication that tells the liver to dump stored sugar into the blood. Keep it in your bag, car, or desk. Someone else might need to use it if you’re too confused to help yourself.
Most people think hypoglycemia only affects diabetics, but it’s more common than you think. People with prediabetes, those on weight-loss drugs like semaglutide, or even healthy folks who go too long without eating can crash. That’s why tracking patterns matters. Did it happen after a workout? After skipping breakfast? After drinking? Write it down. Your doctor can adjust your meds or meal plan. And if you’ve had a severe episode — like fainting or needing someone else to give you glucagon — you need a plan. That means teaching family, coworkers, or friends what to do. Don’t wait for the next episode to figure it out.
What you’ll find below are real, practical guides from people who’ve been there. From how to use a glucagon kit without panicking, to what foods actually help stabilize blood sugar long-term, to the hidden meds that can cause lows even if you’re not diabetic. These aren’t theory pieces. They’re step-by-step, no-fluff instructions for when your blood sugar drops and you need to act — fast.
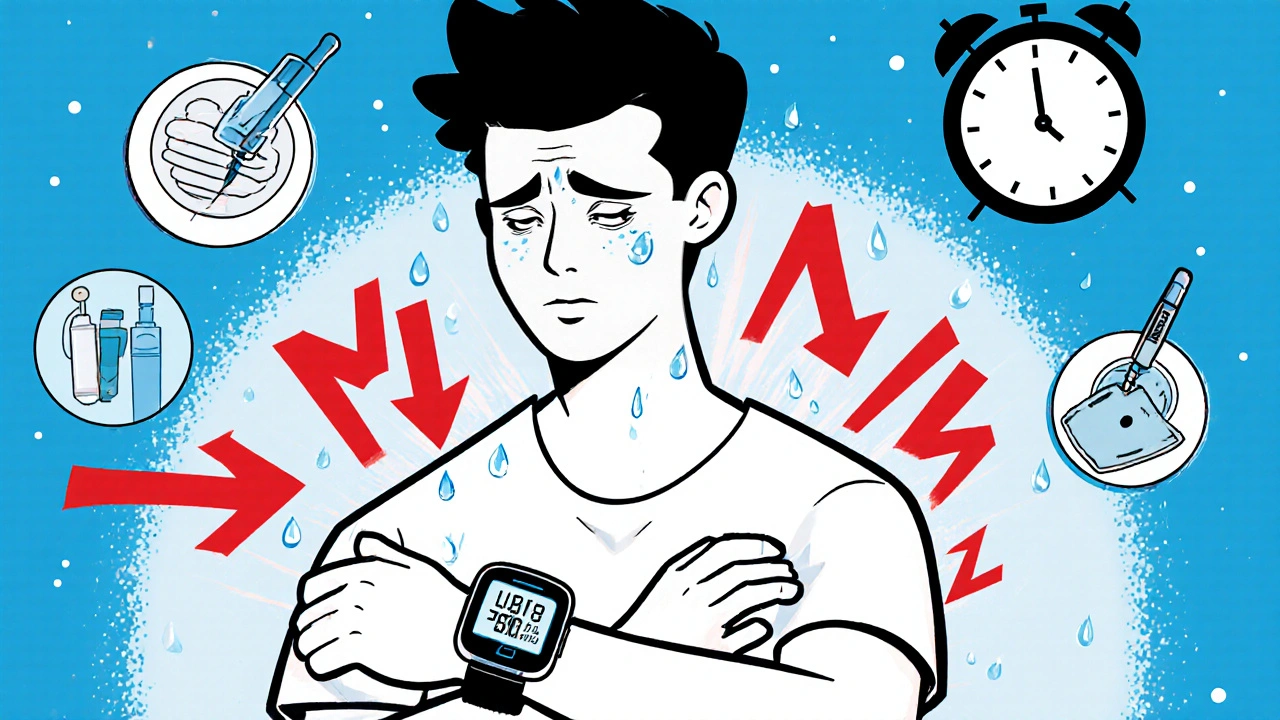

Hypoglycemia: How to Recognize, Treat, and Prevent Low Blood Sugar
Learn how to recognize, treat, and prevent low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) in people with diabetes. Understand symptoms, emergency treatment with glucose and glucagon, and modern prevention tools like CGMs.
View More