SSRI: What They Are, How They Work, and What You Need to Know
When you hear SSRI, Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors are a class of antidepressants that increase serotonin levels in the brain to improve mood and reduce anxiety. Also known as serotonin reuptake inhibitors, they’re the most prescribed type of antidepressant in the U.S. and Europe—not because they’re magic, but because they work for most people with fewer side effects than older options. If you’ve ever been told to try an SSRI for depression, OCD, or panic attacks, you’re not alone. Millions take them every year, and many find relief where other treatments failed.
SSRIs don’t change your personality. They don’t make you feel "high" or numb. What they do is help your brain use serotonin more efficiently. Serotonin is a chemical that helps regulate mood, sleep, and anxiety. When levels are low, you might feel down, restless, or overwhelmed. SSRIs like fluoxetine, a common SSRI also sold as Prozac, used for depression, OCD, and bulimia, sertraline, often called Zoloft, frequently prescribed for depression and social anxiety, and escitalopram, marketed as Lexapro, known for its clean side effect profile block the reabsorption of serotonin, leaving more of it active in your brain. It’s not instant—most people notice changes after 2 to 6 weeks. That’s why doctors tell you to stick with it, even when you feel worse at first.
Side effects are real, but often mild and temporary. Nausea, dry mouth, sleep changes, and sexual dysfunction are common in the first few weeks. For some, weight gain or increased anxiety shows up early. These usually fade. But if they don’t, or if you feel more suicidal in the first month (a rare but serious risk, especially in teens and young adults), talk to your doctor right away. SSRIs aren’t for everyone, and they shouldn’t be stopped cold turkey—tapering matters. They also interact with other meds, like certain painkillers, blood thinners, and even some herbal supplements. That’s why your doctor needs a full list of everything you take.
The posts below cover real-world issues people face with SSRIs: how side effects show up over time, how they interact with other drugs like mood stabilizers, what to do when they don’t work, and how to manage the emotional and physical changes that come with them. You’ll find clear, no-fluff advice on what to expect, when to worry, and how to make the most of treatment—without hype or jargon.
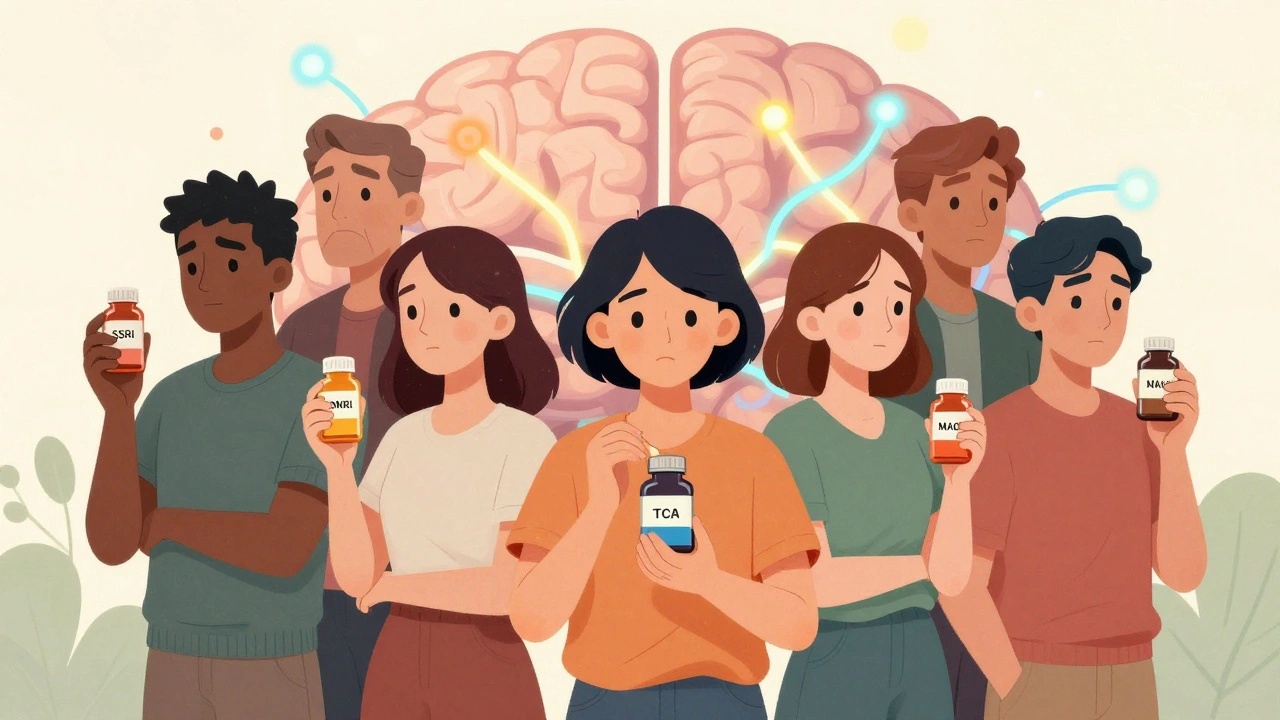

Antidepressants: Types and Safety Profiles for Patients
Antidepressants help millions manage depression and anxiety, but they come with side effects and risks. Learn the main types, how long they take to work, common side effects like weight gain and sexual dysfunction, and what to do if they don't work.
View More